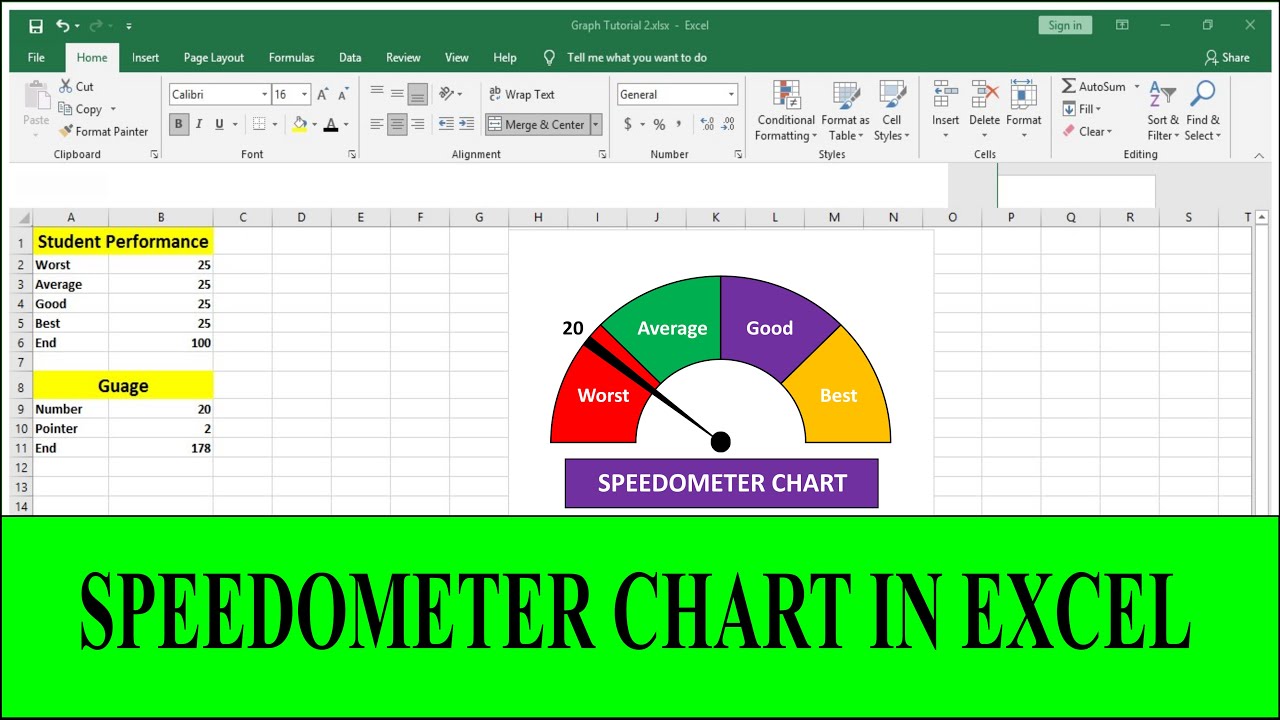
The speedometer chart is a powerful visual tool that has become increasingly popular in data visualization and business intelligence. Its unique circular design, resembling a car's speedometer, offers an intuitive way to represent data performance, trends, and thresholds. Whether you're tracking KPIs, measuring progress, or presenting critical metrics, speedometer charts make complex data easy to understand at a glance.
In today's fast-paced world, decision-makers need quick insights to drive meaningful actions. The speedometer chart provides a real-time snapshot of data, helping stakeholders identify areas of success and aspects that require attention. Its dynamic visuals not only enhance presentations but also simplify decision-making processes across industries like finance, marketing, healthcare, and manufacturing.
This article delves into the intricacies of speedometer charts, exploring their structure, applications, and benefits. We'll also answer common questions, provide actionable tips for creating effective speedometer charts, and discuss best practices to ensure your data visualization efforts stand out. Let's dive in and unlock the potential of this invaluable tool for your next project!
Table of Contents
- What is a Speedometer Chart?
- How Does a Speedometer Chart Work?
- History and Evolution of Speedometer Charts
- Why Use a Speedometer Chart?
- Key Elements of a Speedometer Chart
- Applications of Speedometer Charts Across Industries
- How to Create a Speedometer Chart?
- Best Practices for Designing Speedometer Charts
- Tools and Software for Building Speedometer Charts
- Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Are Speedometer Charts Always Effective?
- How Do Speedometer Charts Differ from Other Charts?
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
What is a Speedometer Chart?
A speedometer chart, also known as a gauge chart, is a type of data visualization tool that represents information in a semi-circular or circular dial. It mimics the design of a car’s speedometer, with a needle indicating a specific value on a scale. This chart is highly useful for visualizing performance metrics, such as sales targets, customer satisfaction levels, or operational efficiency.
The speedometer chart is particularly effective in situations where you need to display a single value within a predefined range. For instance, if you're tracking monthly sales performance, the chart can provide a quick overview of whether you're underperforming, meeting, or exceeding your target. This makes it an exceptional tool for dashboards and presentations.
Key Features of a Speedometer Chart
- Simple and intuitive representation of data.
- Highlights performance thresholds (e.g., low, medium, high).
- Easily customizable to fit various use cases.
- Real-time visualization for dynamic data monitoring.
Who Uses Speedometer Charts?
Speedometer charts are widely used by business professionals, analysts, and decision-makers. Their versatility makes them suitable for industries ranging from finance and marketing to healthcare and automotive. With their ability to present data concisely, they are often featured in executive dashboards, reporting tools, and decision-support systems.
How Does a Speedometer Chart Work?
The speedometer chart works by translating data into visual elements that are easy to interpret. It typically consists of a circular dial divided into colored segments, each representing a specific range or category. A needle or pointer indicates the current value within the range, providing immediate insights into the data’s performance.
Components of a Speedometer Chart
The following are the primary components of a speedometer chart:
- Dial: The semi-circular or circular area displaying the scale.
- Needle: A pointer indicating the specific value being measured.
- Scale: A numerical or categorical range displayed on the dial.
- Color Zones: Segments of the dial indicating performance categories (e.g., green for good, yellow for caution, red for poor).
How to Interpret a Speedometer Chart?
Interpreting a speedometer chart is straightforward. The position of the needle on the scale indicates the data's current value. The color zones provide context, making it easy to identify whether the value is within an acceptable range or requires attention. For instance, if the needle is in the green zone, the performance is satisfactory. In contrast, a needle in the red zone signals underperformance.
History and Evolution of Speedometer Charts
Speedometer charts have their roots in the analog gauges used in automobiles and machinery. These gauges provided a simple yet effective way to monitor performance metrics such as speed, fuel levels, and temperature. As technology advanced, the concept of analog gauges was adapted for data visualization in the digital realm.
In the early days of data visualization, speedometer charts were primarily used in mechanical and industrial settings. However, with the rise of business intelligence tools and dashboard software, their application expanded to include business, healthcare, education, and more. Today, speedometer charts are a staple in modern data visualization, thanks to their simplicity and effectiveness.
Modern Innovations
Modern speedometer charts have evolved to include interactive features, such as real-time updates, dynamic scaling, and customizable color schemes. Advanced tools like Microsoft Power BI, Tableau, and Google Data Studio have made it easier than ever to create and use speedometer charts in various contexts.
Why Use a Speedometer Chart?
Speedometer charts are an invaluable tool for visualizing performance metrics and trends. Their intuitive design allows users to grasp complex data at a glance, making them ideal for both novice and experienced data analysts. Here are some reasons why you should consider using a speedometer chart:
Advantages of Speedometer Charts
- Clarity: Provides a clear and concise representation of data.
- Engagement: Captures the audience's attention with its visually appealing design.
- Actionable Insights: Highlights areas that require immediate attention.
- Versatility: Suitable for various industries and use cases.
When Should You Use a Speedometer Chart?
Speedometer charts are best used in scenarios where you need to display a single metric within a predefined range. Examples include:
- Tracking sales performance against targets.
- Measuring customer satisfaction scores.
- Monitoring key performance indicators (KPIs) in real-time.
- Visualizing progress toward a specific goal.
Key Elements of a Speedometer Chart
To create an effective speedometer chart, it's essential to understand its key elements and how they contribute to its functionality. Below are the main components and their roles:
Dial and Scale
The dial serves as the chart's primary display area, while the scale provides the numerical or categorical range. Together, they form the foundation of the speedometer chart.
Needle and Pointer
The needle or pointer is the most critical element, indicating the data's current value. Its position on the scale determines the performance level.
Color Zones
Color zones enhance the chart's interpretability by categorizing performance levels. For instance, green may represent satisfactory performance, yellow indicates caution, and red signals a problem.
Data Labels
Data labels provide additional context, such as numerical values or percentage scores, making the chart more informative.
Applications of Speedometer Charts Across Industries
Speedometer charts are versatile tools with applications across various industries. Here are some examples of how they are used:
Finance
- Tracking financial performance metrics like revenue, profit margins, or expenses.
- Monitoring investment portfolio performance.
Marketing
- Measuring campaign effectiveness.
- Tracking website traffic and conversion rates.
Healthcare
- Monitoring patient satisfaction scores.
- Tracking hospital resource utilization.
Manufacturing
- Visualizing production efficiency.
- Tracking equipment performance metrics.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the main purpose of a speedometer chart?
The main purpose of a speedometer chart is to provide a quick, visual representation of data performance within a predefined range, making it easier to interpret complex metrics.
2. Can speedometer charts be used for multi-metric analysis?
Speedometer charts are best suited for single-metric analysis. For multi-metric analysis, consider using bar charts, line charts, or other visualization tools.
3. What software can I use to create a speedometer chart?
You can create speedometer charts using tools like Microsoft Excel, Tableau, Power BI, or Google Data Studio. These platforms offer customizable options for designing effective charts.
4. Are there any limitations to using speedometer charts?
Yes, speedometer charts are less effective for large datasets or multi-dimensional analysis. They are best used for simple, single-metric visualizations.
5. How can I make my speedometer chart more engaging?
To make your speedometer chart more engaging, use contrasting colors, interactive features, and clear labels. Ensure the chart aligns with your audience's needs and preferences.
6. What industries benefit the most from speedometer charts?
Industries like finance, marketing, healthcare, and manufacturing benefit significantly from speedometer charts due to their ability to provide actionable insights quickly.
Conclusion
Speedometer charts are a game-changer in the world of data visualization. Their intuitive design, combined with their ability to provide real-time insights, makes them an indispensable tool for professionals across industries. By understanding their structure, applications, and best practices, you can harness the power of speedometer charts to elevate your data storytelling and decision-making processes.
Whether you're a business analyst, marketer, or healthcare professional, the speedometer chart offers a versatile and impactful way to present your data. Start incorporating speedometer charts into your dashboards and presentations today and experience the difference they can make!
You Might Also Like
Smoking Bali: A Cultural And Modern PerspectiveEssential Guide To The Importance And Applications Of Edge Barrier
Lori Powell: A Trailblazing Talent Redefining Success
Benefits And Features Of Alkaline 88: A Premium Water Choice
Everything You Need To Know About Ros Wedding: A Dreamlike Celebration
Article Recommendations
- The Inspiring Journey Of Kim Woo Bin 2015ndashpresent A Tale Of Resilience And Growth
- Unveiling The Truth About Jyoti Amge Relationships
- Temporary Replacement Part 2 Exploring Effective Solutions